NOTE: To perform operations on this page, the user must be a member of the NRTADMIN group, or be assigned to a role with Tier 2 access to Control Center. For more information about the specific operations allowed, refer to Understanding tiers.
The iManage Work system can open, read, and modify many types of documents. This includes popular file types, such as Microsoft Word documents docx, Excel spreadsheets xlsx, along with less common document types, and even custom document types, such as a format proprietary to the organization.
To associate a document type to an application that can read it, two resources work together: File types, and file handlers.
File types define lists of types of documents based on their application extension. That is the documents suffix such as Microsoft Word documents of .docx, or Adobe Acrobat documents of .pdf.
File handlers define lists of applications that can open specified file types. This ties an application, such as Microsoft Word to a file type such as .docx.
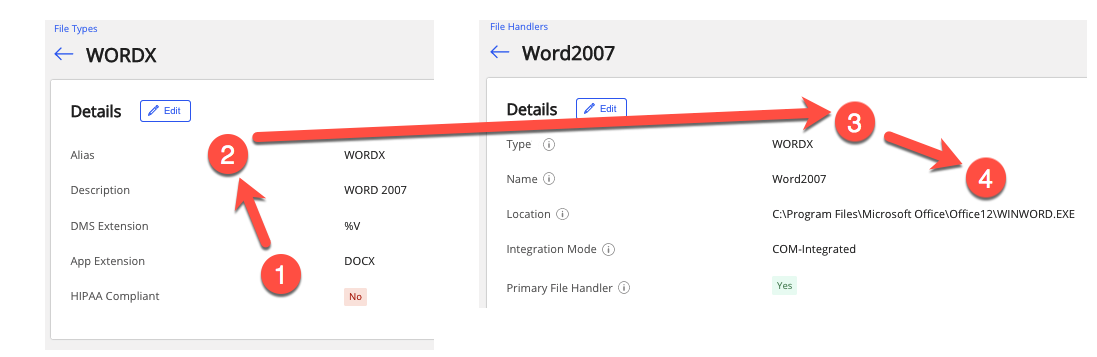
As an example, the following defines a Word .docx document to the application Microsoft Word. The display shows the association of a file type to its corresponding file handler for a Word document .docx.
In the file type resource, the App Extension, DOCX, in step 1, is assigned the Alias of WORDX, in step 2.
The file handler resource completes the assignment by making the association of the type, WORDX, in step 3, to be the same as the alias from file type, step 2. The application is specified in the Location, in step 4.
The two resources allow the application to open the document type. For example, after the file type and file handler is defined, selecting a .docx document within iManage Work displays that document in the preview window. This system doesn't apply to editing documents with iManage Work For Windows. In that case, when the document is checked out, the editing occurs on the user's Microsoft Windows computer and according to Windows' governance of document handling.
More than one file type may be assigned to be opened by Microsoft Word. Each file type requires two separate entries. For example, a document type of .doc may be assigned an alias of Word2007. A text file of document type .txt may be assigned an alias of TEXT. In each case, a separate file handler is required. File types can also be associated with more than one application. For example, a txt file may be associated with both Microsoft Word, and Windows' Notepad.exe. However, one of those file handlers must be marked as the primary application. For more information about how to map document types to the same application, refer to Mapping multiple file types to an application.
On the File Types page, you see a table that displays information about all file types along with their metadata values. Here, you can perform the following:
Search for the required file type using the Search field.
Filter by HIPAA Compliant or App Extension fields.
Add a file type using the Add a File Type feature.
Edit a particular file type's metadata values using the Edit feature.
Enable or disable HIPAA compliance for single or multiple filetypes using the HIPAA Compliant feature.
Delete single or multiple file types using the Delete feature.
View details of a file type using the View feature.
Searching for file types
On the ribbon bar, you see the following Search option that you can use to search by Alias and Description.
Filtering file types
Option | Sub-option | Description |
|---|---|---|
HIPAA Compliant |
| Choose yes to list the file types that have the value set to Yes and the other way around. |
App Extension | NA | Enter the App extension name or any keyword that matches the App extension name, and select Apply. The filtered values get displayed on the screen. For example, to filter all occurrences of the |
Adding a file type
Select +Add File Type. The Add File Types dialog is displayed.
Enter the following information and select Save. A new file type gets added to the Library.
Table: File type metadata
Field | Description |
|---|---|
Alias | Specifies the name by which documents of this type are identified. This name must match the Type value from a file handler.
|
Description | Specifies the description of the file type. |
DMS Extension | Specifies the file name extension that iManage uses to store a document of this type. The default value is %V. If %V is entered as the DMS extension, iManage uses the document’s version number as the file name extension. For example, if the document number is 157, document version is 2, iManage stores the file as 157.2. For more information, see Default Document Types in iManage Work Server Administration Guide. The DMS Extension may not be required depending on the iManage Work environment. For more information, see your iManage Work system administrator. |
App Extension | Specifies the extension that iManage should add to the file name for the document when it's exported, checked-out, emailed, or downloaded. iManage recommends setting the App Extension for a file type to that recognized by the document's assigned application. For example, use DOCX for a Word document. You can use the same extension for multiple file types. |
HIPAA Complaint | Specifies to encrypt document of this file type. If set to Yes, the document will be encrypted. If set to No, the document won't be encrypted. However, see below for additional information. This is the default value. See below for additional information. This is called data at rest encryption and is compliant to HIPAA and other American statutes. This encryption protects sensitive information from accidental or wrongful disclosure. A document will be encrypted if at least one of the following methods applies.
There's no additional effect if more than one condition applies. |
Editing a file type
This option is available on the:
ribbon bar (select file types to see this option on the ribbon bar)
kebab menu (select on the icon adjacent to each file type)
context menu (Right-click a file type to see this option)
Use one of the preceding options and select Edit. The Edit <item-id> dialog appears. It displays the details listed in table File type metadata.
Enabling/disabling HIPAA compliant option
Single file type
This option is available on the:
ribbon bar (select a file type to see this option on the ribbon bar)
kebab menu (select on the icon adjacent to each file type)
context menu (hover on a file type, and right-click to see this option)
For example, let us use the context menu option to enable the HIPAA compliant option.
Scenario: A file type's HIPAA compliant option is disabled (value is set to NO)
Solution: Right-click a file type and select Enable HIPAA Compliant. The HIPAA Compliant option for the file type gets enabled. The updated value automatically reflects in the table for the file type.
Multiple file types
This option is available on the ribbon bar when you select file types.
Select file types. You see HIPAA Compliant drop-down list on the ribbon bar, select it. This lists Yes and No options.
Select the required option. A confirmation message appears. Read and confirm the action. The updated value gets reflected in the table for all the selected file types.
NOTES:
To modify the HIPAA Compliant value for more file types, repeat the steps in this section.
If you want to modify HIPAA Compliant value of a single file type, you can do this by following the information provided in the previous section.
Deleting file types
Single file type
This option is available on the:
ribbon bar (select a file type to see this option on the ribbon bar)
kebab menu (select on the icon adjacent to each file type)
context menu (Right-click a file type to see this option)
Use one of the preceding options and select Delete. Confirm the action to continue or abort.
NOTE: The Database transaction failed; see Administrator error message appears if the class you are trying to delete is still in use by any other object.
Multiple file types
This option is available on the ribbon bar when you select file types.
Select file types on the ribbon bar and select Delete.
Confirm the action to continue or abort.
NOTE: In case of any error, the error messages appear. You can view or download the messages using the Download as CSV option.
Viewing file type details
This option is available on the:
ribbon bar (select a file type to see this option on the ribbon bar)
kebab menu (select on the icon adjacent to each file type)
context menu (Right-click a file type to see this option)
Use one of the preceding options and select View. The <File_Type_ID> page opens. Details of the selected file types are displayed.
NOTE: Use the Edit button to edit metadata values except the Alias.